Use of super
keyword comes in java when inheritance is implemented i.e. when we have super
class and sub classes as explained in the topic Inheritance in Java.
Usage are as
explained below:
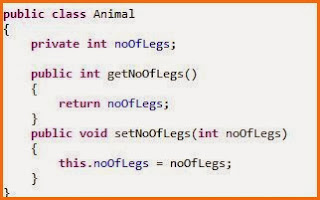
1. To call a super class method :
Normal method call:
When we want to call a method of
super class in a sub class, it can be done by using super.mathodname(). It is demonstrated in below example:
 |
| Parent and child class |
 |
| reference of subclass calling sub class method |
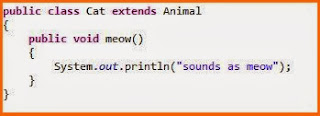
Overridden method call:
When the overriding method needs
to call the overridden method of the parent class, it can be called using super.sameMethodName().
It is demonstrated in below example:
Consider the super class from above example.Subclass has overridden the super class method and in the overridden method, it has called the same method of super class using super.
It is demonstrated in below example:
Consider the super class from above example.Subclass has overridden the super class method and in the overridden method, it has called the same method of super class using super.
 |
| sub class overriding super class method method() |
 |
| output |
2.
To explicitly call the super class constructor(both default and paramaterized) : Though it is not needed because the super class constructor is implicitly called from the sub class constructor.
Default constructor is called in below manner :
Note : while calling constructor of base class from sub class constructor, the super() must be the first statement.
Similarly paramarized constructor can be called.
3.
To
access non private super class members : All non private members in parent class can be accessed using super keyword as shown in below example :